Japan Markets ViewStock Investment Using Share Buyback Progress Data
Nov 13, 2023
Summary
- Share Buybacks Data Provided by QUICK
In addition to share buyback resolution data, QUICK provides progress data showing the status of corporate share buybacks. - Stock Investment Considering the Progress of Market Repurchase, etc.
Favorable investment performance could be observed in the stocks with a share buyback progress rate of more than 20% and less than 60%, which indicates that a certain amount of shares have been repurchased in the initial buyback period and further buybacks can be expected. - Stock Investment Using Tender Offer Repurchase Information
Higher investment performance was shown in the stocks with the total amount of the planned purchase was neither small nor large, i.e., between 2% and 10% of the market capitalization.
Introduction
When a company announces plans to repurchase its own shares, the stock price is expected to rise as the planned volume of shares will be purchased. This article, continuing from the previous issue, discusses the impact of listed companies’ share buyback data on stock investment. Using the Share Buybacks Data provided by QUICK, F-index, a data analysis consulting service provider in Japan, has conducted a verification study.
[Related Articles]
- Equity Investment in Companies Implementing Share Buybacks:
Trends in Share Buybacks in Japan - Stock Investment Strategies Using Share Buyback Information:
Investment Strategy Considering Share Buyback Size, Purchase Price, etc.
This article examines the impact of using share buyback progress status on stock investment. This case study uses the data on the share buyback progress status (Progress Status File) provided by QUICK.
Information on Share Buybacks
The Progress Status File records the share buyback methods. Share buybacks come mainly in two methods: purchase through stock exchanges, including off-auction purchase (market repurchase, etc.); and tender offer repurchase, in which a company purchases its own shares directly from shareholders by announcing the number of shares to purchase, purchase price, and other details.
Companies conducting an market repurchase, etc., periodically announce the progress of the repurchase (usually every month) after the announcement of share buyback plans. Therefore, the Progress Status File can be used to determine the trend of selective buying in the stock market at a given point in time. For example, the file enables the users to know whether, at the time of the progress status announcement, there is still a large number of shares to be repurchased, and the demand for shares is likely to be stimulated after the announcement; or whether the share buyback is proceeding smoothly with the majority of the planned number of shares already repurchased, and the demand for the shares after the announcement is waning.
On the other hand, when a company uses a tender offer to repurchases its own shares, the details of the repurchase are announced at the start of and the results are disclosed only at the end of the tender offer repurchase.
Stock Investment Considering the Progress of Market Repurchase, etc.
Figure 1 shows the distribution of the share buyback progress rates from January to the end of December 2022 for the stocks with their initial buyback period during the same period. Here, the share buyback progress rate refers to the ratio of the number of shares repurchased during the relevant buyback period to the number of shares originally planned to be repurchased. Specifically, it represent to the ratio of the number of shares repurchased during the initial buyback period to the number of shares originally planned to be repurchased.
Figure 1: Distribution of Share Buyback Progress Rates during the Initial Buyback Period
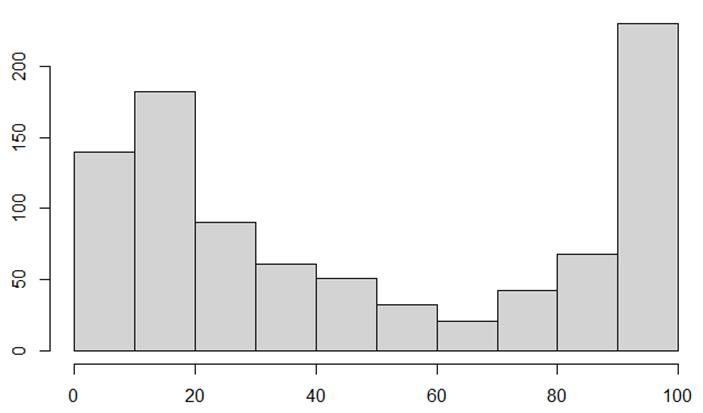
There were 302 cases in which the progress rate was already 80% or more during the initial buyback period, accounting for 32.93% of the total. This indicates that there are many cases where a large number of shares are repurchased immediately after a share buyback announcement is made. Even considering the stock demand stimulated by share buybacks, if most of the planned number of shares to be repurchased has already been purchased, the demand for shares thereafter is not expected to be significant. Expectations of stock price appreciation due to the share buyback would not grow. Thus, it is assumed that expectations of stock price appreciation after the status announcement vary according to the progress rate during the initial buyback period. Based on this assumption, we examined stock investment using the share buyback progress rates.
Stock Investment Using Share Buyback Progress Rate
[Rule]
- Purchase the shares at the market open on the following day of the share buyback progress announcement since such an announcement is often made after market close
- Sell the shares on the last business day not exceeding one month after the purchase date to evaluate the investment performance
Specifically, Resona Holdings (8308) released a notice on December 1, 2022, regarding the status of share buyback. The company repurchased 10,120,000 shares on the Tokyo Stock Exchange from November 14 to November 30, 2022. This represents 25.3% of the total 40,000,000 shares planned to be repurchased. A 13.14% return could be obtained by purchasing the shares at 639.2 yen at the market open on December 2, the day after the share buyback status announcement, and selling them at the closing price of 723.2 yen on December 30, approximately one month later. Since the return of TOPIX over the same period is -3.94%, the active return can be calculated to be 17.08%.
Table 1 summarizes the one-month investment performance after the share buyback announcement by share buyback progress rate for the 917 cases with the initial buyback period in 2022.
Table 1: One-month Stock Investment Performance by Share Buyback Progress Rate during the Initial Buyback Period
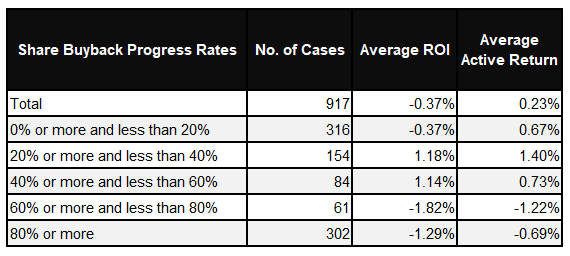
In cases where the progress rate is more than 60%, i.e., a company acquired most of the originally planned number of shares to be repurchased in the initial buyback period, the share demand may have been preempted. This may be why the subsequent stock price movements have been poor, with negative average return on investment and average active return. On the other hand, the average investment return and average active return are both positive for deals where a certain amount of shares have been repurchased in the initial buyback period with the progress rate between 20% and 60%, in other words, for deals where the number of shares repurchased is expected to grow further. Deals with the progress rates of less than 20% are generally not performing well, perhaps because they give the impression that share buybacks are not progressing as expected. These results suggest that favorable performance can be obtained by investing in the stocks whose share buyback status during the initial buyback period showed promising future performance.
Stock Investment Using Tender Offer Repurchase Information
In the case of tender offer repurchase, the progress status is not disclosed. Thus, focusing on the total acquisition price, we examined the stock investment performance based on the ratio of the total acquisition price to the market capitalization at the time of information disclosure (the acquisition price ratio). First, Figure 2 summarizes the distribution of acquisition price ratios for the 16 cases of tender offer share repurchase announced in 2022.
Figure 2: Distribution of Total Acquisition Price for Tender Offer Repurchase Announced in 2022
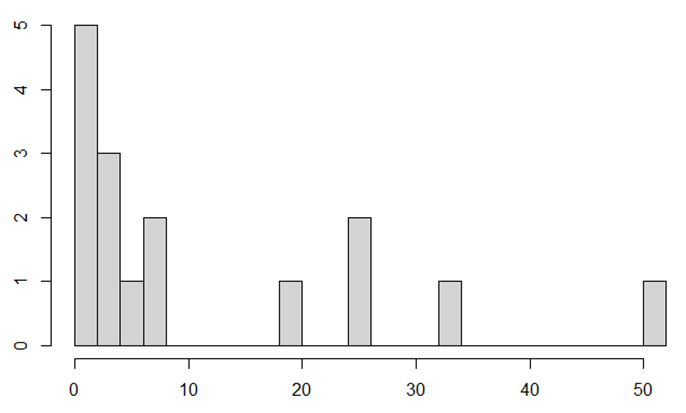
Five cases involve large-scale tender offer repurchase, amounting to 10% or more of the market capitalization. In addition, 11 cases represent repurchase amounting to only a few percent of the market capitalization. Of these, five are small-scale tender offer repurchase cases representing less than 2% of the total market capitalization.
Next, we calculated the investment return rates and the average active return versus TOPIX when shares were purchased at the market open of the day following the tender offer repurchase announcement and sold at the closing price one month later. Table 2 summarizes the results by acquisition price ratio.
Table 2: One-Month Stock Investment Performance by Acquisition Price Ratio at the Time of Tender Offer Repurchase Announcement
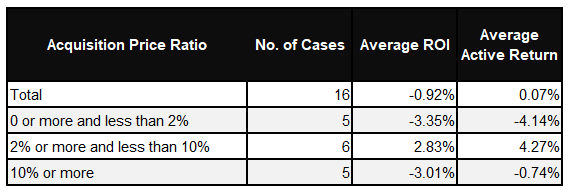
For the five large-scale tender offer repurchase cases with an acquisition price ratio of 10% or more and the five small-scale cases with an acquisition price ratio of less than 2%, both average investment return and average active return were negative, indicating poor investment performance. On the other hand, for the medium-scale tender offer repurchase cases, with the acquisition price ratio between 2% and 10%, both average investment return and average active return were positive, showing favorable investment performance. The results indicate that small-scale tender offer repurchase does not stimulate demand for the stock in question, and large-scale tender offer repurchase does not provide a positive signal for market trading, and neither of them leads to stock price appreciation.
Conclusion
This article examined the stock investments using the data on the share buyback progress status (Progress Status File) provided by QUICK. The file provides information on the following two share buyback methods.
The information on market repurchase, etc., indicated that favorable performance could be obtained by investing the stocks with the share buyback progress status in the initial buyback period showing signs of continued buybacks. The information also suggested that the stock prices tend to fall for companies that have repurchased most of their planned number of shares in the initial buyback period and have announced progress that would preempt future demand for their shares. For such stocks, short selling is expected to generate additional earnings.
Since information on tender offer repurchase is released only at the beginning and after the end of the repurchase, only the information at the beginning of the repurchase can be used when planning stock investment strategies. A tendency for stock price declines was confirmed in the following two cases: cases where the total amount of the planned buyback is very small relative to the market capitalization, which cannot give a favorable impact on the stock prices; and cases with very large total amount relative to market capitalization, which would give a unfavorable impact on the stock prices. For tender offer repurchases, it was shown that high performance may be achieved if the total amount of the planned repurchase is neither small nor large, i.e., between 2% and 10% of the total market capitalization.
Share Buybacks Data on QUICK Data Factory
https://corporate.quick.co.jp/data-factory/en/product/data029/




