Japan Markets ViewStock Investment Strategies Using Share Buyback Information
Feb 16, 2023

Introduction
QUICK collects historical data on share buybacks from the information disclosed by listed companies in Japan. Using the data, F-index, a data analysis consulting service provider in Japan, conducted a verification study. Following the previous article, this article examines the impact of companies’ share buyback information on equity investment. In the previous article, we confirmed that simply using share buyback information is not enough to achieve favorable investment performance. This article explores the effect of investment strategies that take into account the details of share buyback information, such as purposes and scale.
Information on Share Buybacks
When a company announces a share buyback, it is recorded in the “Share Buyback Resolution Information.” Such information provided by QUICK contains the name of the company making an announcement (securities code) and additional information on the share buyback, including the following eight items:
(i) Repurchase period, (ii) Number of shares repurchased, (iii) Repurchase price, (iv) Repurchase price ratio, (v) Estimated acquisition unit price, (vi) Deviation rate of the estimated acquisition unit price, (vii) Board resolution date, and (viii) Announcement date.
This article examines investment strategies that take into account not only the fact that a share buyback has been announced, but also the details of the buyback by using the items listed above.
Scale of Share Buybacks
The scale of buyback varies depending on the purpose of the company’s share buyback. The scale, simply in terms of monetary value, can be confirmed using (iii) Repurchase price. However, it is important to compare the scale with the size of the company. Given this, (iv) Repurchase price ratio shows the ratio of the repurchase price to the market capitalization as of the day before the board resolution date.
In considering the impact of share buyback information on stock prices, investors are generally concerned about the pricing of treasury stock by the companies. Whether the board of directors considers the treasury stock price is above the market price (i.e., whether they believe the stock is worth more than the market price) or whether they perceive the market stock price is overvalued would be an important observation to make in order to determine the future trend of the stock price. In particular, since buyback orders for treasury stock are generated, it is the stock price based on actual demand, which is different from the so-called forecast stock price. Investors cannot overlook this information. Since a company announcing a share buyback does not specify the repurchase price, (v) Estimated acquisition unit price is calculated by dividing the repurchase price by the number of shares repurchased. It is only meaningful to compare this unit price with the market stock price. Thus, the deviation from the closing price of the day prior to the board resolution date is provided as (vi) Deviation rate of the estimated acquisition unit price.
This means that companies planning to repurchase at a higher price than the market stock price can be identified by selecting the companies with a positive (vi) Deviation rate of the estimated acquisition unit price.
Timing of Share Buyback Announcement
Usually, companies unveil their intention to repurchase their own shares after the board of directors makes its resolution. Therefore, (viii) Announcement date is set on the same day or within a few days of (vii) Board resolution date. However, in some cases, the actual data shows (viii) Announcement date is considerably later than (vii) Board resolution date. Even in the recent three years from 2020 to 2022, there are 46 cases recorded that the announcements were made more than 30 days after the board resolution date. The majority of these lags are caused by changes to the terms of previously announced share repurchases. The companies making these changes include those reducing their share buyback scale due to poor repurchase performance, those increasing their share buyback scale driven by successful repurchases, or those shortening the planned repurchase period. In order to focus on the impact on investment in companies that have announced share buybacks, this article targets investments only in companies whose (viii) Announcement date is within seven days from (vii) Board resolution date.
Purposes of Share Buybacks
The purposes of share buybacks include strengthening management resources and enhancing capital efficiency. Among the various purposes, some buybacks are conducted to dispose of fractional shares of less than one share generated by corporate actions (such as mergers, reverse stock splits). In this case, the scale of repurchase is extremely small compared to ordinary share buyback cases. In fact, (iv) Deviation rate of the estimated acquisition unit price is recorded at 0%. Although an in-depth examination of share buybacks is not conducted in this article, extraordinary cases with an extremely small acquisition size are excluded from the investment target.
Investment Strategy Development and Performance Evaluation
As stated so far, each company has a different scale and purpose for implementing share buybacks. Here, we examine the “effect on investment when considering the conditions” of equity investment in companies that have announced share buybacks by investing only in the companies meeting the following conditions.
The three conditions as below are set for this study.
[Condition 1] Companies with a large scale of share buyback ((iv) Deviation rate of the estimated acquisition unit price of 7% or more)
[Condition 2] Companies seeking to acquire at a unit price higher than the market stock price ((vi) Deviation rate of the estimated acquisition unit price of 7% or more)
[Condition 3] Information freshness (companies with (viii) Announcement date within seven days from (vii) Board resolution date)
The companies meeting the above three conditions are investment targets. By setting
[Condition 1], exceptional buybacks, such as a case to dispose of fractional shares, are excluded from the scope of investment.
The investment operation procedure is as follows. Two investment periods are set: buying the shares at the market open of the business day following the date of the respective company’s announcement date of share buyback and selling them at the market close of the same day (one-day investment period) or of one week later (one-week investment period). Then, (A) Expected return (average of returns), (B) Risk (standard deviation of returns), and (C) Expected return per unit of risk ((A) divided by (B)) are calculated. Since the data from different investment periods are aggregated, the market influences are removed by evaluating performance based on the difference from the TOPIX return over the same investment period (active return).
First, let us take a look at the performances of equity investment in all companies that announced share buybacks during the same period without following the investment strategy described above. Table 1 shows the performances when investing in all companies that announced share buybacks during the same period.
Table 1: Performance Evaluation without Specific Investment Strategies (Without Annualized Conversion)
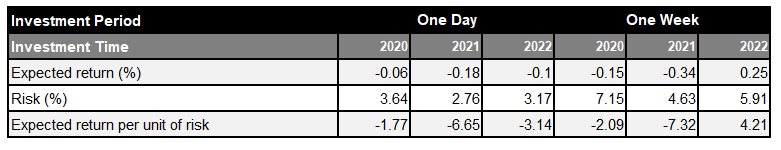
A positive expected return can be confirmed only for the one-week investment period in 2022, and negative returns are shown for the other investment periods. In other words, the results indicate that better performances can be attained by investing in stocks (investing in TOPIX) without considering stock buyback information. Next, let us look at the performances when investing in stocks by narrowing down the target to companies satisfying the above three conditions among those that announced share buybacks. Table 2 summarizes the performance indicators for each investment time and period.
Table 2: Evaluation of Performances with Equity Investment Strategies Considering the Set Conditions for Share Buybacks (Without Annualized Conversion)
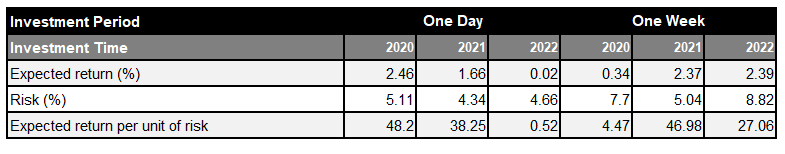
Performance improvements can be observed, and active returns are attained for all investment times and periods. The results suggest that, rather than simply investing in stocks, better performance can be obtained by appropriately narrowing down the scale and purpose of buybacks of the companies implementing buybacks. This is particularly the case with investments in companies that have a large buyback scale and announced a buyback at a notional price higher than the market stock price.
Conclusion
This article evaluated the performances of equity investment using share buyback information. The results shows that better stock investment performances can be obtained by considering the details of the buyback, such as scale of the buyback and whether the company plans to buy back shares at a price higher than the market stock price, rather than simply the information that a stock repurchase will be implemented.
In this article, we examined an investment method that uses share buyback information only at the time of the announcement of a buyback. However, as discussed in the section “Timing of Share Buyback Announcement,” the terms of a share buyback may be revised after its initial announcement. It is also interesting to see how the stock price is affected by whether or not the company’s buyback is proceeding as planned until the terms of the buyback are revised. Considering that the impact on stock prices based on actual demand occurs when actual purchases are being made in the stock market, the progress of share buybacks is deemed to have an impact on stock prices. “Repurchase progress” is available as the data on the progress of share buybacks. It would also be interesting to examine the impact on stock prices arising from share buyback progress as well as the revisions to the terms of share buybacks.
QUICK provides the share buybacks data introduced in this article via API.
Share Buybacks Data on QUICK Data Factory
https://corporate.quick.co.jp/data-factory/en/product/data029/




