Japan Markets ViewManufacturers’ Production Forecasts Made Possible Using Factory Visitation Data
Apr 04, 2024
Honda Motor’s (7267, Honda) vehicle driving data can potentially be used to predict manufacturers’ production activities. If the number of vehicles visiting each company’s production plant could be ascertained, it would be possible to anticipate production status.
An analysis was conducted using the “Honda Drive Data Service (Customer Index)” (hereafter, “Customer Index”) provided by QUICK. This index calculates data on visits to retail stores and factories by obtaining Honda’s vehicle driving data with the consent of users. The Customer Index is linked to the stock codes of listed companies, facilitating financial and economic data analysis. Previously, this index focused on B2C stock data, but is being expanded to include B2B stock data as well.
Labor input is one of many factors that determine corporate production activities. The Customer Index, which indicates the number of visitors to a factory, is strongly related to the number of employees coming to work. If the Customer Index is useful as a surrogate variable for labor input, it would be possible to forecast production activities using the Index.
Correlation between Labor Input and Production Activities Varies across Industries
Before looking at the relationship between the Customer Index and production activities, we investigate the relationship between labor input and production activities. We examined the correlation coefficient between labor input by industry (= total actual hours worked x number of employees), calculated using monthly labor statistics, and the year-on-year change in the industrial production index of Indices of Industrial Production (IIP).
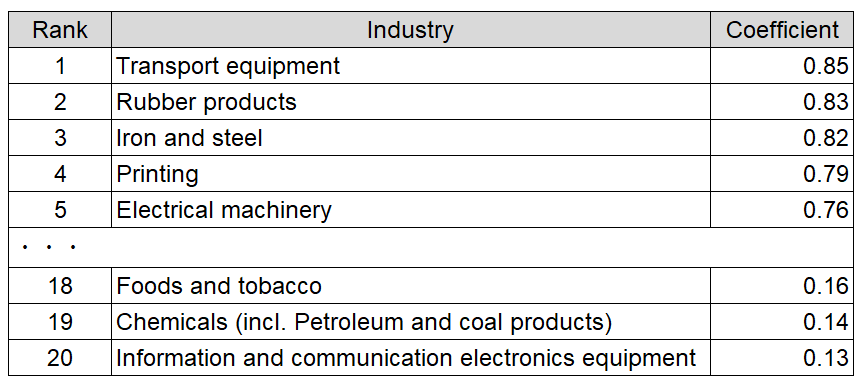
The results show that correlation varies across industries. Among them, transport equipment and rubber products exhibit high correlation. These industries are labor-intensive, and labor input is an important factor in determining production status. On the other hand, little correlation is observed in the industries of information and communication electronics equipment as well as chemicals (incl. petroleum and coal products), where automation is highly developed. In these industries, labor input is considered less important in production activities.
Therefore, production in labor-intensive industries would likely be predicted if a surrogate variable for labor input could be created using the Customer Index.
Use of Data for Predicting Tire Manufacturers’ Production
In labor-intensive industries, labor input is an important factor in determining production status. For example, the production status of the rubber products industry, especially automobile tire manufacturers, could be determined using the Customer Index.
Manpower Is Indispensable for Tire Manufacturing
Tire manufacturing is a labor-intensive industry, and the manufacturing process involves a great deal of manual labor. With recent advances in automation and technological innovation, machines and robots are utilized in the manufacturing process. However, highly skilled workers still play an important role in quality inspections and other processes. Overall, there remain elements where manpower is indispensable and highly sophisticated work is required.
Visitors to the Four Major Manufactures Increase in March and October
In the Japanese tire industry, major manufacturers are globally competitive, represented by companies such as The Yokohama Rubber (5101), Toyo Tire (5105), Bridgestone (5108), and Sumitomo Rubber Industries (5110). These companies have a dominant share of the Japanese tire market. The following is a comparison of the Customer Index (visitors to production plants) of the four major companies, compiled on a monthly basis.
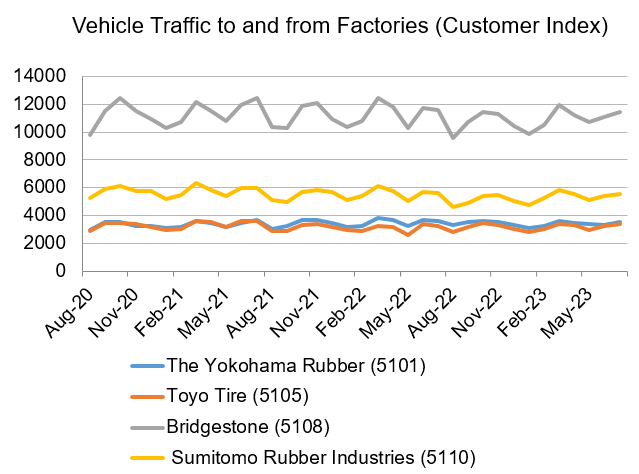
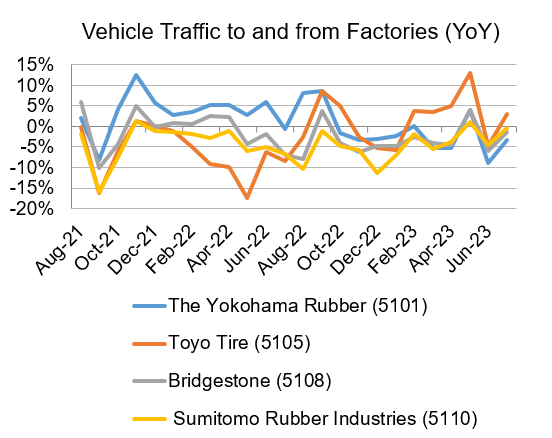
Each company’s Customer Index was compiled on a monthly basis, and the results show a strikingly similar trend of increase or decrease by the time of year for the four major companies. In particular, vehicle traffic to and from the factories increased in March and October.
Generally, tire production tends to increase during the periods when summer and winter tires are replaced, peaking in March and October. This coincides with the timing of increased vehicle traffic into and out of the factories. Given the above, it is possible that the Customer Index reflects the increase or decrease in production in the tire industry as a whole.
Reading Ahead Corporate Production Activities Using the Index
We examined whether there is a link between the Customer Index and tire production volume. We compiled automobile tire production volume based on the Current Survey of Production published monthly by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. Then, we compared the data with the Customer Index of the four major tire manufacturers on a monthly basis.
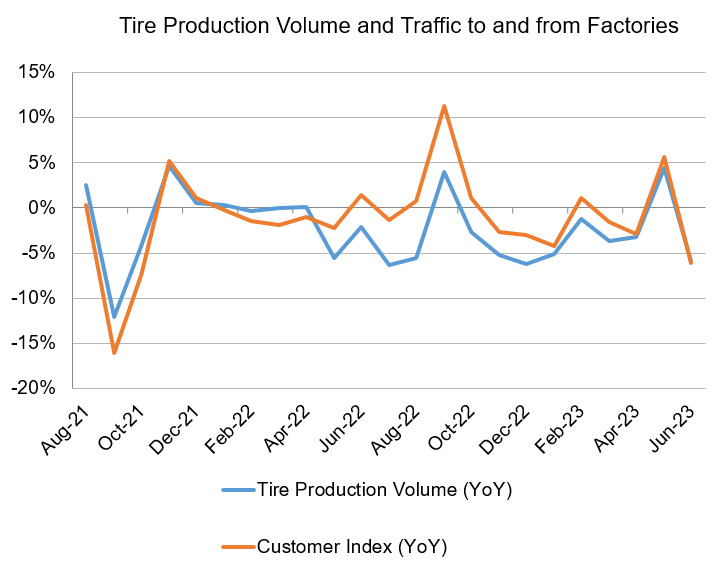
A high correlation was found between automobile tire production volume and changes in vehicle traffic into and out of the factories, with a correlation coefficient of 0.82. In a labor-intensive industry, it would be possible to estimate production status based on the Customer Index.
There is a time lag of up to two months until the figures are released in the Current Survey of Production. For example, preliminary figures for January 2024 are released at the end of February, and final figures at the end of March. On the other hand, the Honda’s Customer Index can be provided on a daily basis. Using the Customer Index, which is linked to production volume, would allow us to predict corporate production activities before the release of government statistics.
Honda Drive Data Service (Customer Index) on QUICK Data Factory
https://corporate.quick.co.jp/data-factory/en/product/data040/




